Viva Resa: Your Gateway to Insightful Living
Discover news, trends, and tips for a vibrant lifestyle.
Eat Big, Lift Bigger: The Bulking Diet Dilemma
Unlock the secrets to bulking up! Discover how to eat big and lift bigger with our ultimate guide to the bulking diet dilemma.
The Ultimate Guide to Building Muscle: Nutrition Tips for Your Bulking Journey
Building muscle effectively requires a comprehensive approach, and nutrition plays a pivotal role in your bulking journey. First and foremost, caloric surplus is essential; you need to consume more calories than you burn to fuel muscle growth. Aim for a modest surplus of about 250-500 calories per day. Focus on macronutrients: prioritize high-quality proteins, such as lean meats, fish, eggs, and legumes, which help repair and build muscle tissue. Additionally, include complex carbohydrates like whole grains and starchy vegetables to provide the energy required for rigorous workouts, alongside healthy fats from sources such as avocados and nuts to support overall health and hormone production.
Hydration is another critical aspect of nutrition during your bulking phase. Drinking enough water enhances performance and recovery, ensuring your muscles stay hydrated. To optimize your long-term muscle-building results, consider implementing a structured meal plan that allows for both consistency and flexibility. Incorporate nutrient-dense snacks between meals, such as protein shakes or Greek yogurt with fruits, to meet your calorie needs without feeling overly full. Remember, tracking your progress through regular measurements can help you adjust your diet as needed. By following these tips, you can set the foundation for a successful bulking journey.
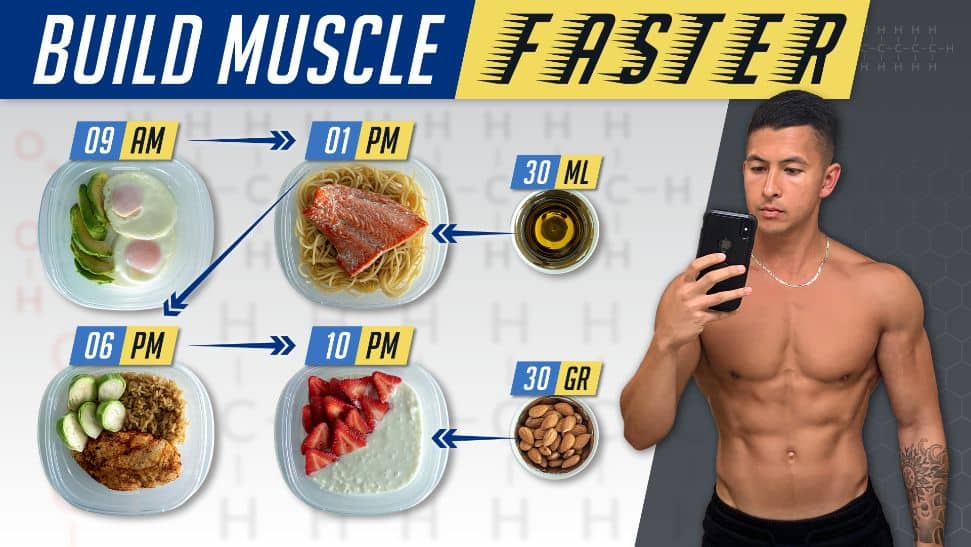
How to Calculate Your Daily Caloric Needs for Optimal Bulking
Calculating your daily caloric needs is essential for anyone looking to optimize their bulking journey. Start by determining your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR), which is the number of calories your body requires at rest to maintain basic bodily functions. You can use the Mifflin-St Jeor equation for this calculation:
- For men: BMR = 10 × weight(kg) + 6.25 × height(cm) - 5 × age(y) + 5
- For women: BMR = 10 × weight(kg) + 6.25 × height(cm) - 5 × age(y) - 161
Once you have your BMR, multiply it by an activity factor to account for your daily physical activity level, ranging from sedentary (1.2) to very active (1.9). This will give you your Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE), which is the number of calories you burn in a day. For effective bulking, aim to consume a surplus of about 250-500 calories over your TDEE.
After calculating your TDEE, focus on the composition of your caloric increase. Prioritize macronutrients by maintaining a balanced diet rich in proteins, healthy fats, and carbohydrates. A common approach is to aim for about 20-30% of your calories from protein, 30-40% from fats, and 40-50% from carbohydrates. For more detailed guidance on macronutrient distribution, check out this Bodybuilding.com article. Remember to track your progress over time, and adjust your caloric intake based on your results to ensure that you are gaining muscle without excessive fat.
Top 5 Common Mistakes to Avoid When Following a Bulking Diet
Embarking on a bulking diet can be an exciting yet challenging journey for those looking to gain muscle mass. However, many find themselves making critical mistakes that hinder their progress. One common error is neglecting to track calorie intake accurately. Many individuals assume they are consuming enough calories to promote muscle growth, but without careful tracking, they often fall short. Utilizing apps or journals to log meals can provide valuable insights and help you stay on course.
Another frequent mistake is focusing solely on large amounts of protein without balancing macronutrients. While protein is essential, carbohydrates and healthy fats play crucial roles in energy levels and hormone production. Consuming a balanced diet not only supports muscle recovery but also aids in maintaining overall health. Incorporating resources like guides on macro distribution can further refine your approach to bulking effectively.